A
A accommodation; adenine; ampere; anode (anodal); anterior; axial; mass number.
A2 aortic second sound (see heart sounds).
a- word element. [L.] without, not.
α alpha, small letter; first letter in the Greek alphabet.
(A-a) Po2 alveolar–arterial oxygen tension difference.
A band filaments of myosin forming a dark (anisotropic) band in the sarcomere.
A-mode amplitude mode. See A-mode ultrasonography.
A–R–F sequence remodeling sequence of bone cell activity; means activation–resorption–formation.
A site see aminoacyl-tRNA binding site.
aa. pl. arteriae [L.] arteries.
āā [Gr.] ana (of each), in prescriptions.
AAALAC Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care.
AAAS American Association for the Advancement of Science.
AaDo2 alveolar-arterial oxygen tension difference.
AAFCO American Association of Feed Control Officials.
AA-MRSA animal-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
AA protein a product of α-globulin and the major protein component of reactive amyloid.
AAHA American Animal Hospital Association.
AALAS American Association of Laboratory Animal Science
AAUAAA sequence see polyadenylation.
AAVC American Association of Veterinary Clinicians.
AAVMC Association of American Veterinary Medical Colleges.
AAVSB American Association of Veterinary State Boards.
Ab antibody. Called also gamma globulin (γ). See immunoglobulin.
ab- word element. [L.] from, off, away from.
a. viral mortality a viral disease of molluscs with a very high mortality rate. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 22).
abamectin a mixture of avermectins derived from Streptomyces avermitilis.
abarticular [ab″ahr-tik′u-l r] not affecting a joint; away from a joint.
r] not affecting a joint; away from a joint.
abarticulation [ab″ahr-tik″u-la′sh n] a dislocation.
n] a dislocation.
abasia [ -ba′zh
-ba′zh ] inability to walk.
] inability to walk.
a. atactica abasia with uncertain movements, due to a defect of coordination.
choreic a. abasia due to chorea of the limbs.
paralytic a. abasia due to paralysis.
spastic a. see paroxysmal trepidant abasia (above).
trembling a., a. trepidans abasia due to trembling of the limbs.
abaxial situated away from the axis of the body, limb or part.
gaunt a. decreased abdominal size.
surgical a. see acute abdomen (above).
a. cavity the body cavity between the diaphragm and the pelvis containing the abdominal organs.

A-1 Pig with distended abdomen due to rectal stricture causing marked distension of the large intestine.
a. lavage see abdominal lavage.
a. pain may arise from an abdominal organ, the peritoneum or be referred as from spinal nerves.
a. silhouette the shape of the abdomen viewed from behind.
a. tunic see tunica flava abdominis.
abdominal sounds [ab-dom′ -n
-n l soundz] sounds heard on auscultation of the abdomen.
l soundz] sounds heard on auscultation of the abdomen.
abdomin(o)- word element, abdomen.
abdominohysterotomy [ab-dom″ -no-his″t
-no-his″t r-ot′
r-ot′ -me] hysterotomy through an abdominal incision.
-me] hysterotomy through an abdominal incision.
abdominoparacentesis [ab-dom″ -no par″
-no par″ -sen-te′sis] abdominocentesis.
-sen-te′sis] abdominocentesis.
abduce to abduct, or draw away.
abducens [ab-doo′s nz] [L.] drawing away; pertaining to a movement away from the midline of the body.
nz] [L.] drawing away; pertaining to a movement away from the midline of the body.
a. nerve see abducent nerve, and Table 14.
abducent [ab-doo′s nt] abducting.
nt] abducting.
a. nerve either of the paired sixth cranial nerves; each arises from the pons and supplies the lateral rectus and retractor bulbi muscles of the eye, allowing for motion. Paralysis of the nerve causes a medial strabismus and absence of third eyelid protrusion when the corneal reflex is tested. See also Table 14.
abduct [ab-dukt′ ] to draw away from an axis or the median plane.
abductor [ab-duk′tor] that which abducts.
aberrant pigment metabolism [ă-ber′ nt pig′m
nt pig′m nt m
nt m -tab′
-tab′ -liz″
-liz″ m] see inherited porphyria.
m] see inherited porphyria.
abiosis [a″bi-o′sis] absence or deficiency of life.
abiotrophic disease [a″bi-o-tro′fik] see abiotrophy.
spinal cord a. see hereditary neuronal abiotrophy of Swedish Lapland dogs (above).
abirritant 1. diminishing irritation; soothing. 2. an agent that relieves irritation.
abirritation [ab-ir- -ta′sh
-ta′sh n] diminished irritability; atony.
n] diminished irritability; atony.
ablactation [ab″lak-ta′sh n] weaning.
n] weaning.
ablastin [a″blas′tin] an antibody that inhibits the reproduction of some protozoan parasites.
ablate [ab-lāt′] to remove, especially by surgical means.
ablatio [ab-la′she-o] [L.] detachment.
a. retinae detachment of the retina.
ablepharia [a″bl -far′e-
-far′e- ] congenital absence of the eyelids.
] congenital absence of the eyelids.
ablepharon [a″blef′ -ron] see ablepharia.
-ron] see ablepharia.
abluent [ab′loo- nt] 1. detergent; cleansing. 2. a cleansing agent.
nt] 1. detergent; cleansing. 2. a cleansing agent.
abnormality [ab″nor-mal′ -te] 1. the state of being unlike the usual condition. 2. a malformation.
-te] 1. the state of being unlike the usual condition. 2. a malformation.
abnutzen pigment see lipofuscin.
abomasal [ab″o-ma′s l] pertaining to, affecting or originating from the abomasum.
l] pertaining to, affecting or originating from the abomasum.
a. dilatation see right abomasal displacement (below).
a. displacement see left abomasal displacement, right abomasal displacement (below).
a. phytobezoar see phytobezoar.
a. rupture see abomasal perforation (above).
a. torsion see abomasal volvulus (below).
a. trichobezoar see trichobezoar.
a. tympany see abomasal bloat (above).
Abondance cattle French breed of dual-purpose cattle, mostly red, some red on belly and extremities.
aboral [ab-or’ l] away from the mouth.
l] away from the mouth.
abortifacient [ -bor″t
-bor″t -fa’sh
-fa’sh nt] 1. causing abortion. 2. an agent that induces abortion.
nt] 1. causing abortion. 2. an agent that induces abortion.
artificial a. voluntary or elective termination of pregnancy. See also parturition induction.
campylobacter a. see infectious abortion (below).
complete a. complete expulsion of all the products of conception.
incomplete a. abortion in which parts of the products of conception are retained in the uterus.
missed a. the animal was diagnosed pregnant, but found later to be open.
septic a. abortion associated with serious infection of the uterus leading to generalized infection.
spontaneous a. abortion occurring naturally. See also spontaneous abortion.
therapeutic a. abortion induced by a veterinarian for medical or other health reasons.
abortive [ -bor’tiv] 1. incompletely developed. 2. abortifacient.
-bor’tiv] 1. incompletely developed. 2. abortifacient.
abortus [ -bor’t
-bor’t s] a dead or nonviable fetus.
s] a dead or nonviable fetus.
ABP see androgen binding protein.
ABPEE acronym for acute bovine pulmonary emphysema–edema. See atypical interstitial pneumonia.
ABR auditory brainstem response.
ABR test abortus-bang-ring test. See also brucellosis testing, milk ring test.
abrachia [ -bra’ke-
-bra’ke- ] congenital absence of the forelimbs.
] congenital absence of the forelimbs.
abrachiocephalia [ -bră″ke-o-s
-bră″ke-o-s -fa’le-
-fa’le- ] acephalobrachia.
] acephalobrachia.
abrasive [ -bra’siv] 1. causing abrasion. 2. an agent that produces abrasion.
-bra’siv] 1. causing abrasion. 2. an agent that produces abrasion.
Abrus [a’br s] pantropical plant genus of the legume family Fabaceae.
s] pantropical plant genus of the legume family Fabaceae.
apical a. a localized suppurative inflammation of tissues about the apex of a tooth root.
cervical a. see vertebral abscess.
diffuse a. a collection of pus not enclosed by a capsule. More properly described as cellulitis.
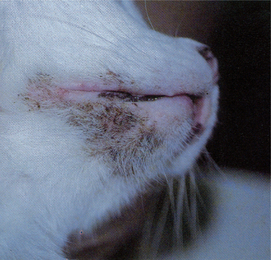
facial subcutaneous a. a disease of cattle eating hay or pasture containing mature grass awns.
gas a. one containing gas, caused by gas-forming bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens.
hepatic a. abscess of the liver caused by a variety of infectious agents.
infraorbital a. occurs in birds as a sequel to chronic upper respiratory infection with sinusitis.
internal abdominal a. see retroperitoneal abscess.
maxillary a. see malar abscess.
miliary a. one of a set of small abscesses; the name derived from millet seed (size).
milk a. abscess of the mammary gland occurring during lactation.
pancreatic a. abscess of the pancreas, most commonly seen as a sequel to pancreatitis.
phoenix a. acute recurrence of a chronic periapical abscess.
primary a. one formed at the seat of the infection.
rete mirabile a. see pituitary abscess.
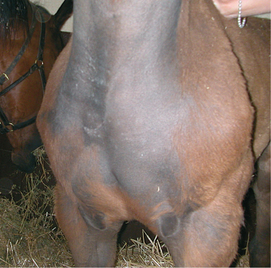
A-5 Pectoral abscess (pigeon fever) with swelling of the left pectoral region and the lower neck.
From McAuliffe SB, Slovis NM, Color Atlas of Diseases and Disorders of the Foal. Saunders, 2008
stitch a., suture a. one developed about a stitch or suture.
abscessation formation of an abscess.
abscission [ab-s ’zh
’zh n] removal of a part or growth by cutting.
n] removal of a part or growth by cutting.
absorbefacient [ab-sor″b -fa’sh
-fa’sh nt] 1. causing absorption. 2. an agent that promotes absorption.
nt] 1. causing absorption. 2. an agent that promotes absorption.
Compton a. effect see Compton effect.
differential a. the difference in the absorption of X-rays by different tissues.
percutaneous a. absorption of drugs or noxious substances through the skin.
absorptive [ab-sorp’tiv] having the power of absorption; involving absorption.
abu nini [Sudanese] see contagious caprine/ovine pleuropneumonia.
abuse [ -būs’] misuse, maltreatment or excessive use.
-būs’] misuse, maltreatment or excessive use.
ABVP American Board of Veterinary Practitioners.
a.c. [L.] ante cibum (before meals).
A. aneura Called also mulga. See acquired melanosis.
A. berlandieri contains tyramine which causes ataxia in sheep and goats. Called also guajillo.
A. cana can accumulate selenium if the soil selenium content is unusually large.
A. catechu cyanogenic plant. See catechu.
A. salicina contains toxic tannins; rarely causes incoordination, recumbency.
false a., black a. see Robinia pseudoacacia.
ACAID anterior chamber-associated immune deviation
acampsia [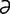 -kamp’se-
-kamp’se-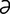 ] rigidity of a part or limb.
] rigidity of a part or limb.
acantha [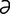 -kan’th
-kan’th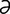 ] thorn[Gr.]; a spine-like structure.
] thorn[Gr.]; a spine-like structure.
acanth(o)- word element. [Gr.] sharp spine, thorn.
acanthocephalans [ -kan″tho-sef’
-kan″tho-sef’ -l
-l ns] members of the phylum Acanthocephala.
ns] members of the phylum Acanthocephala.
acanthocephalid see acanthocephalans.
acanthocytosis [ -kan″tho-si-to’sis] the presence in the blood of acanthocytes.
-kan″tho-si-to’sis] the presence in the blood of acanthocytes.
a. bullosa see epidermolysis bullosa.
infundibular keratinizing a. see intracutaneous cornifying epithelioma.
frictional a. see acanthosis nigricans (below).
Acanthospermum plant genus of the Asteraceae family; originated in tropical America.
Acanthospiculum [ak″an-tho spik’u-l m] see Onchocerca.
m] see Onchocerca.
acapnia decrease of carbon dioxide in the blood.
acarapisosis a disease of the adult honey bee (Apis mellifera) and possibly other Apis species caused by the honey bee tracheal mite Acarapis woodi, which parasitizes the respiratory system resulting in moderate to high mortality. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 22).
acarbia [a-kahr’be- ] decrease of bicarbonate in the blood.
] decrease of bicarbonate in the blood.
acardia [a-kahr’de- ] a developmental anomaly with absence of the heart.
] a developmental anomaly with absence of the heart.
acardiacus [a″kahr-di’ -kus] [L.] having no heart.
-kus] [L.] having no heart.
otodectic a. see Otodectes cynotis.
pulmonary a. see Pneumonyssoides.
acarid [ak’ -rid] a tick or a mite of the order Acarina.
-rid] a tick or a mite of the order Acarina.
Acarina [ak″ -ri’n
-ri’n ] an order of arthropods (class Arachnida), including mites and ticks.
] an order of arthropods (class Arachnida), including mites and ticks.
acarinosis [ -kar″
-kar″ -no’sis] any disease caused by mites.
-no’sis] any disease caused by mites.
acarodermatitis [ak″ -ro-dur″m
-ro-dur″m -ti’tis] skin inflammation due to bites of parasitic mites (acarids).
-ti’tis] skin inflammation due to bites of parasitic mites (acarids).
Acaroidea a superfamily of the order Acarina.
acaryote 1. non-nucleated. 2. a non-nucleated cell.
accelerated conduction syndrome see accessory tract atrioventricular conduction.
linear a. very high energy (1–20 mega volt) X-ray machine to administer radiation therapy treatment.
serum prothrombin conversion a. (SPCA) clotting factor VII; see proconvertin.
acceptor [ak-sep’t r] a substance that unites with another substance.
r] a substance that unites with another substance.
hydrogen a. the molecule accepting hydrogen in an oxidation–reduction reaction.
access [ak’ses] surgical term for the ease of reaching the target organ or site in an operation.
Accipiter genus of birds of prey that includes goshawks and sparrowhawks.
acclimation [ak″l -ma’sh
-ma’sh n] the process of becoming accustomed to a new environment.
n] the process of becoming accustomed to a new environment.
amplitude of a. the accommodative range of an eye.
histological a. changes in morphology and function of cells following changed conditions.
accreditation given a stamp of legitimacy and dependability by an authorized agency.
ACE angiotensin-converting enzyme.
acellular [a-sel’u-l r] not cellular in structure.
r] not cellular in structure.
acelomate [a-se’l -māt] having no celom or body cavity.
-māt] having no celom or body cavity.
acephalobrachia [a-sef″ -lo-bra’ke-
-lo-bra’ke- ] congenital absence of the head and forelimbs.
] congenital absence of the head and forelimbs.
acephalocardia [a-sef″ -lo-kahr’de-
-lo-kahr’de- ] congenital absence of the head and heart.
] congenital absence of the head and heart.
acephalocardius [a-sef″ -lo-kahr’de-us] a fetus without a head or heart.
-lo-kahr’de-us] a fetus without a head or heart.
acephalochiria [a-sef″ -lo-ki’re-
-lo-ki’re- ] congenital absence of the head and forefeet.
] congenital absence of the head and forefeet.
acephalogastria [a-sef″ -lo-gas’tre-
-lo-gas’tre- ] congenital absence of the head, thorax and stomach.
] congenital absence of the head, thorax and stomach.
acephalopodia [a-sef″ -lo-po’de-
-lo-po’de- ] congenital absence of the head and hindfeet.
] congenital absence of the head and hindfeet.
acephalopodius [a-sef″ -lo-po’de-us] a fetus without a head or hindfeet.
-lo-po’de-us] a fetus without a head or hindfeet.
acephalorachia [a-sef″ -lo-ra’ke-
-lo-ra’ke- ] congenital absence of the head and vertebral column.
] congenital absence of the head and vertebral column.
acephalothoracia [a-sef″ -lo-tho-ra’se-
-lo-tho-ra’se- ] congenital absence of the head and thorax.
] congenital absence of the head and thorax.
acephalous [a-sef’ -l
-l s] headless.
s] headless.
acephalus [a-sef’ -l
-l s] a headless fetus.
s] a headless fetus.
Acer [a’s r] trees of the family Aceraceae.
r] trees of the family Aceraceae.
acervuline [ -sur’vu-līn] aggregated; heaped up; said of certain glands.
-sur’vu-līn] aggregated; heaped up; said of certain glands.
acetabular [as″ -tab’u-l
-tab’u-l r] pertaining to the acetabulum.
r] pertaining to the acetabulum.
a. cup the acetabular component of a total artificial hip arthroplasty.
a. dysplasia see hip dysplasia.
a. plate an orthopedic plate designed specifically for repair or fixation of the acetabulum.
acetabulectomy [as″ -tab″u-lek’t
-tab″u-lek’t -me] excision of the acetabulum.
-me] excision of the acetabulum.
acetabuloplasty [as″ -tab’u-lo-plas″te] plastic repair of the acetabulum.
-tab’u-lo-plas″te] plastic repair of the acetabulum.
acetal [as’ -t
-t l] an organic compound formed by a combination of an aldehyde with an alcohol.
l] an organic compound formed by a combination of an aldehyde with an alcohol.
acetate [as’ -tāt] a salt of acetic acid.
-tāt] a salt of acetic acid.
a. base cellulose acetate sheet used as support or base for X-ray film.
acetic [ -se’tik] pertaining to vinegar or its acid; sour.
-se’tik] pertaining to vinegar or its acid; sour.
acetoacetate [ -se″to-as’
-se″to-as’ -tāt] see acetoacetic acid.
-tāt] see acetoacetic acid.
acetokinase [as″ -to ki’nās] enzyme catalyzing the phosphorylation of acetate using ATP.
-to ki’nās] enzyme catalyzing the phosphorylation of acetate using ATP.
a. poisoning in companion animals causes narcosis, gastritis and renal and hepatic damage.
acetonemia [as″ -to-ne’me-
-to-ne’me- ] ketonemia; see ketosis.
] ketonemia; see ketosis.
acetonuria [as″ -to-nu’re-
-to-nu’re- ] ketonuria.
] ketonuria.
acetophenazine a phenothiazine, similar to chlorpromazine, used as a tranquilizer.
acetophenetidin see phenacetin.
Acetosella vulgaris Rumex acetosella.
acetyl [as’ -t
-t l, as’
l, as’ -tēl″
-tēl″  -se’t
-se’t l] the monovalent radical, CH3CO, a combining form of acetic acid.
l] the monovalent radical, CH3CO, a combining form of acetic acid.
acetylandromedol [as″ -t
-t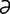 l-, as″
l-, as″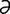 -tēl-an-drom’
-tēl-an-drom’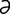 -dol] grayanotoxin (andromedotoxin).
-dol] grayanotoxin (andromedotoxin).
acetylcoenzyme A [as’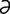 -t
-t l, as″
l, as″ -tēl’ ko-en’zīm] see acetyl CoA.
-tēl’ ko-en’zīm] see acetyl CoA.
N-acetyl loline alkaloid a compound thought to contribute to fescue poisoning.
acetyl-β-methylcholine see methacholine.
acetylpromazine [ -se’t
-se’t l pro’m
l pro’m -zēn] acepromazine.
-zēn] acepromazine.
acetylsalicylic acid [ -se’t
-se’t l-sal″
l-sal″ -sil’ik] see aspirin.
-sil’ik] see aspirin.
AcG accelerator globulin (clotting factor V).
esophageal a. see megaesophagus.
acheilia [ -ki’le-
-ki’le- ] a developmental anomaly with absence of the lips.
] a developmental anomaly with absence of the lips.
acheiria [ -ki’re-
-ki’re- ] a developmental anomaly with absence of the forefeet.
] a developmental anomaly with absence of the forefeet.
achillobursitis [ -kil″o-b
-kil″o-b r-si’tis] inflammation of the bursae about the gastrocnemius tendon.
r-si’tis] inflammation of the bursae about the gastrocnemius tendon.
achillodynia [ -kil″o-din’e-
-kil″o-din’e- ] pain in the Achilles tendon or its bursa.
] pain in the Achilles tendon or its bursa.
achillorrhaphy [ak″ -lor’
-lor’ -fe] suturing of the gastrocnemius tendon.
-fe] suturing of the gastrocnemius tendon.
achillotenotomy [ -kil″o-t
-kil″o-t -not’
-not’ -me] surgical division of the gastrocnemius tendon.
-me] surgical division of the gastrocnemius tendon.
achlorhydria [a″klor-hi’dre- ] absence of hydrochloric acid from gastric juice.
] absence of hydrochloric acid from gastric juice.
Acholeplasma [a″ko-le-plaz’m ] a genus of the class Mollicutes and related to the genus Mycoplasma.
] a genus of the class Mollicutes and related to the genus Mycoplasma.
acholia [a-ko’le- ] lack or absence of bile secretion.
] lack or absence of bile secretion.
acholuria absence of bile pigments from the urine.
inherited congenital a. see achondroplastic dwarfism.
inherited a. dwarfism see achondroplastic dwarfism.
inherited a. with hydrocephalus see bulldog calves.
achromat [ak’ro-mat] an achromatic microscope objective.
achromatous [ -kro’m
-kro’m -tus] colorless.
-tus] colorless.
achromaturia [ -kro″m
-kro″m -tu’re-
-tu’re- ] colorless state of the urine.
] colorless state of the urine.
achromia [ -kro’me-
-kro’me- ] the lack or absence of normal color or pigmentation, as of the skin.
] the lack or absence of normal color or pigmentation, as of the skin.
achromocyte [ -kro’mo-sīt] a red cell artifact that stains more faintly than intact red cells.
-kro’mo-sīt] a red cell artifact that stains more faintly than intact red cells.
achromoderma amelanosis; lack of pigment in the skin.
achromophil [ -kro’mo-fil] see achromatophil.
-kro’mo-fil] see achromatophil.
Achtheres a genus of the class Crustacea which parasitize freshwater fish.
Achyla a genus of fungi which cause disease in fish reared by fish culturists and aquarists.
achylia [ -ki’le-
-ki’le- ] absence of hydrochloric acid and enzymes in the gastric secretions.
] absence of hydrochloric acid and enzymes in the gastric secretions.
achymia [ -ki’me-
-ki’me- ] deficiency of chyme.
] deficiency of chyme.
acicular [ -sik’u-l
-sik’u-l r] acicularis [L.]; needle-shaped.
r] acicularis [L.]; needle-shaped.
bile a’s steroid acids derived from cholesterol. See also bile acids.
a. hydrolases major group of enzymes present in lysosomes.
inorganic a. an acid containing no carbon atoms.
keto a’s compounds containing the groups CO (carbonyl) and COOH (carboxyl).
a. phosphatase see acid phosphatase.
acid–antigen plate test [as’id an’t -j
-j n plāt] see rose bengal test.
n plāt] see rose bengal test.
acid citrate dextrose [as’id sit’rāt dek’strōs] see ACD.
acid-detergent fiber [as’id de-tur’j nt fi’b
nt fi’b r] see acid-detergent fiber2.
r] see acid-detergent fiber2.
acidemia [as″ -de’me-
-de’me- ] abnormal acidity of the blood.
] abnormal acidity of the blood.
acidic [ -sid’ik] of or pertaining to an acid; acid-forming.
-sid’ik] of or pertaining to an acid; acid-forming.
acidifying solution a solution used in fluid therapy for alkalosis.
acidophile [ -sid’o-fīl″] see acidophil.
-sid’o-fīl″] see acidophil.
acidophilic [as″ -do-fil’ik] 1. easily stained with acid dyes. 2. growing best on acid media.
-do-fil’ik] 1. easily stained with acid dyes. 2. growing best on acid media.
hepatocellular a. bodies see cytosegresome formation.
compensated a. condition in which the compensatory mechanisms have returned the pH toward normal.
hypercapnic a. respiratory acidosis.
ruminal a. acidosis caused by an altered metabolic state, usually lactic acidosis, in the rumen.
uremic a. see metabolic acidosis (above).
aciduric [as″ -doo’rik] capable of growing well in extremely acid media.
-doo’rik] capable of growing well in extremely acid media.
acinar [as’ -n
-n r] pertaining to or affecting an acinus or acini.
r] pertaining to or affecting an acinus or acini.
acinetic [as″ -net’ik] akinetic.
-net’ik] akinetic.
aciniform [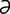 -sin’
-sin’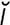 -form] grapelike.
-form] grapelike.
acinitis [as″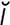 -ni’tis] inflammation of the acini of a gland.
-ni’tis] inflammation of the acini of a gland.
acinous [as’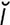 -n
-n s] made up of acini.
s] made up of acini.
ACLAM American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine.
aclasia, aclasis [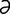 -kla’zh
-kla’zh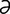 , ak’l
, ak’l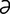 -sis] pathological continuity of structure, as in chondrodystrophy.
-sis] pathological continuity of structure, as in chondrodystrophy.
acme [ak’me] the critical stage or crisis of a disease.
contagious equine a. see Canadian horsepox.
interdigital a. see interdigital pyoderma.
acneiform [ak’ne-form] resembling acne.
acokantherosis the state of being poisoned by Acokanthera spp.
Acomys cahirinus see spiny mouse.
aconite [ak’ -nīt] see Aconitum.
-nīt] see Aconitum.
acoprosis absence or paucity of feces in the intestines.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
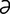 -m
-m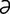 n] the portion of the body between the thorax and the pelvis containing the abdominal cavity and abdominal organs. See also abdominal.
n] the portion of the body between the thorax and the pelvis containing the abdominal cavity and abdominal organs. See also abdominal. -n
-n l] pertaining to, affecting or originating in the abdomen. See also abdominal paracentesis, abdominal sounds.
l] pertaining to, affecting or originating in the abdomen. See also abdominal paracentesis, abdominal sounds. -no-sen-te′sis] paracentesis of the abdomen. See also abdominal paracentesis.
-no-sen-te′sis] paracentesis of the abdomen. See also abdominal paracentesis. -no skōp] an endoscope that, by passage through the abdominal wall into the abdominal cavity, permits direct visualization of the abdomen and its contents. See also laparoscope.
-no skōp] an endoscope that, by passage through the abdominal wall into the abdominal cavity, permits direct visualization of the abdomen and its contents. See also laparoscope.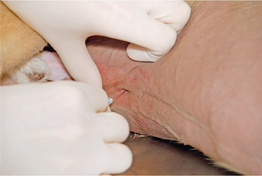
 -nos′k
-nos′k -pe] examination of the abdomen and its contents with an endoscopic instrument inserted through the abdominal wall. See also laparoscopy.
-pe] examination of the abdomen and its contents with an endoscopic instrument inserted through the abdominal wall. See also laparoscopy. n] the act of abducting; the state of being abducted. For a digit, the drawing away from the axis of the limb.
n] the act of abducting; the state of being abducted. For a digit, the drawing away from the axis of the limb. r-a′sh
r-a′sh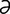 n] 1. deviation from the normal or usual. 2. imperfect refraction or focalization of a lens, e.g. the lens of the eye.
n] 1. deviation from the normal or usual. 2. imperfect refraction or focalization of a lens, e.g. the lens of the eye.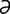 -fe] inherited developmental defect resulting in a lack of a biologic substance within a cell type which is necessary for the maintenance of that cell and which leads to premature degeneration.
-fe] inherited developmental defect resulting in a lack of a biologic substance within a cell type which is necessary for the maintenance of that cell and which leads to premature degeneration. n] 1. separation or detachment; extirpation; eradication. 2. removal, especially by cutting.
n] 1. separation or detachment; extirpation; eradication. 2. removal, especially by cutting. -si′tis] inflammation of abomasum; occurs as part of many gastroenteritides but seldom diagnosed as a separate condition. The organ’s location aboral to the forestomachs provides some protection against dietary insults. Abomasitis caused by Clostridium sordelli is an emerging problem in sheep in Great Britain, manifest with sudden death. Lambs between 6 and 10 weeks are particularly at risk. See also abomasum.
-si′tis] inflammation of abomasum; occurs as part of many gastroenteritides but seldom diagnosed as a separate condition. The organ’s location aboral to the forestomachs provides some protection against dietary insults. Abomasitis caused by Clostridium sordelli is an emerging problem in sheep in Great Britain, manifest with sudden death. Lambs between 6 and 10 weeks are particularly at risk. See also abomasum.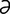 -me] surgical opening of the abomasum, usually to remove impacted food or foreign material, especially phytobezoars.
-me] surgical opening of the abomasum, usually to remove impacted food or foreign material, especially phytobezoars.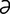 -bort’ ] 1. to arrest prematurely a disease or developmental process. 2. to expel the products of conception before the fetus is viable.
-bort’ ] 1. to arrest prematurely a disease or developmental process. 2. to expel the products of conception before the fetus is viable. -bor’sh
-bor’sh n] premature expulsion from the uterus of the products of conception; termination of pregnancy before the fetus is viable.
n] premature expulsion from the uterus of the products of conception; termination of pregnancy before the fetus is viable. -bra’zh
-bra’zh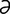 n] a wound caused by rubbing or scraping the skin or mucous membrane. A ‘skinned knee’ and a ‘rope burn’ are common examples.
n] a wound caused by rubbing or scraping the skin or mucous membrane. A ‘skinned knee’ and a ‘rope burn’ are common examples.
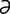 ] the distance of the x-coordinate along the horizontal or x-axis from the vertical or y-axis in a rectangular coordinate system. Also, now commonly used as an alternate term for the horizontal or x-axis of a graph.
] the distance of the x-coordinate along the horizontal or x-axis from the vertical or y-axis in a rectangular coordinate system. Also, now commonly used as an alternate term for the horizontal or x-axis of a graph.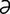 l] pertaining to the effect on nonirradiated tissue resulting from irradiation of other tissues of the body.
l] pertaining to the effect on nonirradiated tissue resulting from irradiation of other tissues of the body.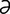 ns] in radiology, a measure of the ability of a medium to absorb radiation, expressed as the logarithm of the quotient of the intensity of the radiation entering the medium divided by that leaving it.
ns] in radiology, a measure of the ability of a medium to absorb radiation, expressed as the logarithm of the quotient of the intensity of the radiation entering the medium divided by that leaving it.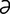 nt] 1. able to take in, or suck up and incorporate. 2. a tissue structure, lymphatic or other vessel, involved in absorption. 3. a substance that absorbs or promotes absorption. Absorbents used pharmaceutically are usually finely ground inert substances applied locally to prevent friction and reduce tissue irritation, e.g. talc, zinc stearate, amixture of boric acid and calciumoxide. Similar substances, e.g. finely ground charcoal, kaolin, are administered orally for the same purposes and also to absorb toxins.
nt] 1. able to take in, or suck up and incorporate. 2. a tissue structure, lymphatic or other vessel, involved in absorption. 3. a substance that absorbs or promotes absorption. Absorbents used pharmaceutically are usually finely ground inert substances applied locally to prevent friction and reduce tissue irritation, e.g. talc, zinc stearate, amixture of boric acid and calciumoxide. Similar substances, e.g. finely ground charcoal, kaolin, are administered orally for the same purposes and also to absorb toxins. n] 1. the act of taking up or in by specific chemical or molecular action; especially the passage of liquids or other substances through a surface of the body into body fluids and tissues, as in the absorption of the end products of digestion into the villi that line the intestine. 2. in radiology, uptake of energy by matter with which the radiation interacts.
n] 1. the act of taking up or in by specific chemical or molecular action; especially the passage of liquids or other substances through a surface of the body into body fluids and tissues, as in the absorption of the end products of digestion into the villi that line the intestine. 2. in radiology, uptake of energy by matter with which the radiation interacts. n] outward rotation of the globe around the line of sight when the eye is at its central primary position.
n] outward rotation of the globe around the line of sight when the eye is at its central primary position. -ka’sh
-ka’sh ] a large genus of trees and shrubs of warm, dry regions, belonging to the legume family Mimosaceae, which provides valuable browse for grazing ruminants but also contains some poisonous plants. About 5% of Australian Acacia spp. are cyanogenic. Acacia spp. capable of causing cyanide poisoning: A. atkinsiana, A. binerva (A. glaucescens), A. blakei, A. burrowii, A. caffra, A. caroleae, A. cheelii (motherumbah), A. concurrens (A. cunninghamii), A. conniana (A. cognata), A. crassa (A. cunninghamii), A. cunninghamii (black wattle), A. curvinervia, A. deanei (A. paucijuga), A. doratoxylon, A. erioloba (camel thorn), A. exilis, A. glaucescens (sally wattle), A. granitica, A. gregii (catclaw), A. lasiocalyx, A. lasiopetala (A. sieberana), A. leiocalyx (A. melanoxylon), A. longifolia, A. longispicata (A. cunninghamii), A. olgana, A. osswaldii, A. polybotrya, A. pulchella, A. pycnostachya, A. schinoides, A. sibina, A. sieberana, A. sparsiflora, A. sutherlandii (A. melaleucoides), A. yorkrakinensis.
] a large genus of trees and shrubs of warm, dry regions, belonging to the legume family Mimosaceae, which provides valuable browse for grazing ruminants but also contains some poisonous plants. About 5% of Australian Acacia spp. are cyanogenic. Acacia spp. capable of causing cyanide poisoning: A. atkinsiana, A. binerva (A. glaucescens), A. blakei, A. burrowii, A. caffra, A. caroleae, A. cheelii (motherumbah), A. concurrens (A. cunninghamii), A. conniana (A. cognata), A. crassa (A. cunninghamii), A. cunninghamii (black wattle), A. curvinervia, A. deanei (A. paucijuga), A. doratoxylon, A. erioloba (camel thorn), A. exilis, A. glaucescens (sally wattle), A. granitica, A. gregii (catclaw), A. lasiocalyx, A. lasiopetala (A. sieberana), A. leiocalyx (A. melanoxylon), A. longifolia, A. longispicata (A. cunninghamii), A. olgana, A. osswaldii, A. polybotrya, A. pulchella, A. pycnostachya, A. schinoides, A. sibina, A. sieberana, A. sparsiflora, A. sutherlandii (A. melaleucoides), A. yorkrakinensis.
 -ka’sh
-ka’sh ] 1. general term for the very large number of species of shrubs and trees in the genus Acacia; many known also generally as wattles in Australia. 2. the dried exudate from Acacia senegal and other Acacia species of African origin, used as an emulsifier, stabilizer and suspending agent. Called also gum arabic and gum acacia.
] 1. general term for the very large number of species of shrubs and trees in the genus Acacia; many known also generally as wattles in Australia. 2. the dried exudate from Acacia senegal and other Acacia species of African origin, used as an emulsifier, stabilizer and suspending agent. Called also gum arabic and gum acacia. -kan″th
-kan″th -me’b
-me’b ] free-living amebae that can cause pneumonia, general systemic infection and encephalomyelitis in animals and humans.
] free-living amebae that can cause pneumonia, general systemic infection and encephalomyelitis in animals and humans. -kan″tho-sef’
-kan″tho-sef’ -l
-l ] a phylum of elongate, mostly cylindrical organisms (thorny-headed worms) parasitic in the intestines of all classes of vertebrates.
] a phylum of elongate, mostly cylindrical organisms (thorny-headed worms) parasitic in the intestines of all classes of vertebrates. -kan″tho-sef″
-kan″tho-sef″ -li’
-li’ -sis] disease caused by infection with members of the phylum Acanthocephala.
-sis] disease caused by infection with members of the phylum Acanthocephala. -kan″tho-sef’
-kan″tho-sef’ -l
-l s] a genus of thorny-headed worms of the family Echinorhynchinae. Includes A. jacksoni (in trout).
s] a genus of thorny-headed worms of the family Echinorhynchinae. Includes A. jacksoni (in trout). -kan″tho-ki″lo-ne’m
-kan″tho-ki″lo-ne’m ] found in body cavities and connective tissue of dogs. Called also Dipetalonema reconditum.
] found in body cavities and connective tissue of dogs. Called also Dipetalonema reconditum. -kan’tho-sīt] an erythrocyte with protoplasmic projections giving it a thorny appearance; results from intravascular erythrocyte fragmentation associated with microangiopathy. Most commonly seen in dogs vasculitis or other vascular anomalies, hemangiosarcomas or liver disease. Morphologically similar to spur cells, but biochemically distinct.
-kan’tho-sīt] an erythrocyte with protoplasmic projections giving it a thorny appearance; results from intravascular erythrocyte fragmentation associated with microangiopathy. Most commonly seen in dogs vasculitis or other vascular anomalies, hemangiosarcomas or liver disease. Morphologically similar to spur cells, but biochemically distinct.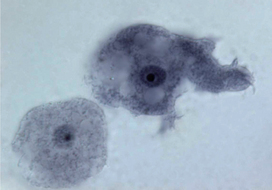
 -sis] loss of cohesion between epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal clefts, vesicles and bullae. Seen in inflammatory, viral, heritable and autoimmune skin diseases, particularly the pemphigus complex.
-sis] loss of cohesion between epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal clefts, vesicles and bullae. Seen in inflammatory, viral, heritable and autoimmune skin diseases, particularly the pemphigus complex. ] a tumor in the prickle cell layer of the skin. See intracutaneous cornifying epithelioma.
] a tumor in the prickle cell layer of the skin. See intracutaneous cornifying epithelioma. -kan’tho-fis] the genus of death adders; includes A. antarcticus (common death adder) and A. pyrrhus (desert death adder).
-kan’tho-fis] the genus of death adders; includes A. antarcticus (common death adder) and A. pyrrhus (desert death adder). -ri’
-ri’ -sis] infestation with arthropod parasites of the order Acarina including the ticks and mites. See also tick infestation.
-sis] infestation with arthropod parasites of the order Acarina including the ticks and mites. See also tick infestation.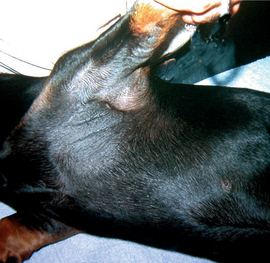
 -kar’
-kar’ -sīd] an agent that destroys ticks and mites. The common ones are the organophosphorus compounds, the synthetic pyrethroids, the carbamates and the macrocyclic lactones. The chlorinated hydrocarbons are no longer much used on farm animals because of the problems with residue in tissues.
-sīd] an agent that destroys ticks and mites. The common ones are the organophosphorus compounds, the synthetic pyrethroids, the carbamates and the macrocyclic lactones. The chlorinated hydrocarbons are no longer much used on farm animals because of the problems with residue in tissues. -rīn] pertaining to or of the nature of members of the order Acarina, including the ticks and mites.
-rīn] pertaining to or of the nature of members of the order Acarina, including the ticks and mites. -rus] a genus of free-living mites, including A. farinae, A. longion, A. siro and A. tawinae; see Tyroglyphus.
-rus] a genus of free-living mites, including A. farinae, A. longion, A. siro and A. tawinae; see Tyroglyphus. r-a″t
r-a″t r] [L.] an agent or apparatus that increases the rate at which something occurs or progresses.
r] [L.] an agent or apparatus that increases the rate at which something occurs or progresses. -re] supplementary or affording aid to another similar and generally more important thing.
-re] supplementary or affording aid to another similar and generally more important thing. -kli″m
-kli″m -t
-t -za’sh
-za’sh n] the adaptation of an animal to the climatic conditions in an area. The ability to adapt in this way is an important characteristic of livestock.
n] the adaptation of an animal to the climatic conditions in an area. The ability to adapt in this way is an important characteristic of livestock. -kom″
-kom″ -da’sh
-da’sh n] adjustment, especially rapid adjustment, of the eye for focusing on objects at various distances. Accomplished by the ciliary body muscles, which (depending on species) alter lens position or shape, globe length, or corneal radius of curvature as needed for distant or near vision.
n] adjustment, especially rapid adjustment, of the eye for focusing on objects at various distances. Accomplished by the ciliary body muscles, which (depending on species) alter lens position or shape, globe length, or corneal radius of curvature as needed for distant or near vision. -kre’sh
-kre’sh n] 1. growth by addition of material. 2. accumulation. 3. adherence of parts normally separated.
n] 1. growth by addition of material. 2. accumulation. 3. adherence of parts normally separated. -se] 1. the closeness with which an observation or a measurement of a variable approximates its true value. An important component of diagnostic tests. An accurate test implies freedom from both random and systematic error. See also precision. 2. degree of conformance between the estimated or measured position of a GPS receiver and its true position. Differential positioning can be used to improve positioning accuracy by determining the positioning error at a known location by comparison to a known reference position.
-se] 1. the closeness with which an observation or a measurement of a variable approximates its true value. An important component of diagnostic tests. An accurate test implies freedom from both random and systematic error. See also precision. 2. degree of conformance between the estimated or measured position of a GPS receiver and its true position. Differential positioning can be used to improve positioning accuracy by determining the positioning error at a known location by comparison to a known reference position. dap’sōn] a sulfone, related to dapsone, used in the treatment of leprosy in humans and atypical mycobacterial infections in animals.
dap’sōn] a sulfone, related to dapsone, used in the treatment of leprosy in humans and atypical mycobacterial infections in animals. -se″no-koo’m
-se″no-koo’m -rol] a warfarin derivative used as an anticoagulant. Called also nicoumalone.
-rol] a warfarin derivative used as an anticoagulant. Called also nicoumalone. -lo-sto’me-
-lo-sto’me- ] congenital absence of the head, with the mouth aperture on the upper aspect of the body.
] congenital absence of the head, with the mouth aperture on the upper aspect of the body. -pro’m
-pro’m -zēn] one of the phenothiazine derivative psychotropic drugs, used in animals as a means of chemical restraint. Its principal value is in quietening and calming frightened and aggressive animals. The standard pharmaceutical preparation, acepromazine maleate, is used extensively in horses, cats and dogs, especially as a preanesthetic agent. Called also acetylpromazine.
-zēn] one of the phenothiazine derivative psychotropic drugs, used in animals as a means of chemical restraint. Its principal value is in quietening and calming frightened and aggressive animals. The standard pharmaceutical preparation, acepromazine maleate, is used extensively in horses, cats and dogs, especially as a preanesthetic agent. Called also acetylpromazine. -sur’vu-l
-sur’vu-l s] pl. acervuli [L.] sandy calcifications in or about the pineal body and choroid plexus.
s] pl. acervuli [L.] sandy calcifications in or about the pineal body and choroid plexus. -tab’u-l
-tab’u-l m] the cup-shaped socket of the hip joint that receives the head of the femur. See also acetabular.
m] the cup-shaped socket of the hip joint that receives the head of the femur. See also acetabular. t-al’d
t-al’d -hīd″] a colorless volatile liquid, CH3CHO, found in freshly distilled spirits, which is irritating to mucous membranes and has a general narcotic action. It is also an intermediate in the metabolism of alcohol.
-hīd″] a colorless volatile liquid, CH3CHO, found in freshly distilled spirits, which is irritating to mucous membranes and has a general narcotic action. It is also an intermediate in the metabolism of alcohol. -se″t
-se″t -min’
-min’ -fen] an analgesic and antipyretic drug in dogs. It is contraindicated for cats because of serious sideeffects which include intravascular hemolysis, methemoglobinemia and hepatic necrosis. Called also paracetamol (INN).
-fen] an analgesic and antipyretic drug in dogs. It is contraindicated for cats because of serious sideeffects which include intravascular hemolysis, methemoglobinemia and hepatic necrosis. Called also paracetamol (INN). t-ahr’sol, as″
t-ahr’sol, as″ t-ahr’sōn] an organic arsenical used as an antiprotozoal agent, especially in turkeys and geese. See also organic arsenic poisoning.
t-ahr’sōn] an organic arsenical used as an antiprotozoal agent, especially in turkeys and geese. See also organic arsenic poisoning. -zol’
-zol’ -mīd] a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to reduce aqueous humor production and thereby intraocular pressure in the treatment of glaucoma.
-mīd] a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to reduce aqueous humor production and thereby intraocular pressure in the treatment of glaucoma. -se″to-
-se″to- -se’tik] CH3COCH2COOH, one of the ketone bodies formed in the body in metabolism of certain substances, particularly in the liver in the oxidation of fats, and utilized in extrahepatic tissues to obtain energy. It is present in the body in increased amounts in abnormal conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and starvation, and in bovine ketosis and pregnancy toxemia of cows and ewes. Occurs in the body as acetoacetate.
-se’tik] CH3COCH2COOH, one of the ketone bodies formed in the body in metabolism of certain substances, particularly in the liver in the oxidation of fats, and utilized in extrahepatic tissues to obtain energy. It is present in the body in increased amounts in abnormal conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and starvation, and in bovine ketosis and pregnancy toxemia of cows and ewes. Occurs in the body as acetoacetate. -to-as’
-to-as’ -t
-t l,
l,  -se’to-as-
-se’to-as- -tēl″ko-a’] intermediate in ketogenesis and utilization of the ketones, β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate. Penultimate intermediate in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids.
-tēl″ko-a’] intermediate in ketogenesis and utilization of the ketones, β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate. Penultimate intermediate in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids. -to-hek’s
-to-hek’s -mīd] a first generation sulfonylurea derivative, used as an oral hypoglycemic agent in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
-mīd] a first generation sulfonylurea derivative, used as an oral hypoglycemic agent in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. -to-hi″droks-am’ik] a hydroxamic acid that specifically inhibits urease; it retards alkalinization of the urine caused by urease-producing bacteria and may inhibit bacterial growth. Used in the prevention and dissolution of uroliths, but in dogs causes a dose-related, reversible hemolytic anemia and blood dyscrasia.
-to-hi″droks-am’ik] a hydroxamic acid that specifically inhibits urease; it retards alkalinization of the urine caused by urease-producing bacteria and may inhibit bacterial growth. Used in the prevention and dissolution of uroliths, but in dogs causes a dose-related, reversible hemolytic anemia and blood dyscrasia. -tōn] a compound, CH3COCH3, with solvent properties and characteristic odor, obtained by fermentation or produced synthetically; it is a by-product of acetoacetic acid. Acetone is one of the ketone bodies produced in abnormal amounts in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, metabolic acidosis, pregnancy toxemia and ketosis of ruminants. Unlike the other ketone bodies, acetone cannot be used by the tissues to generate energy and is excreted as a waste product in the urine and by exhalation. The characteristic fruity odor on the breath of animals with ketosis is due to the exhalation of acetone.
-tōn] a compound, CH3COCH3, with solvent properties and characteristic odor, obtained by fermentation or produced synthetically; it is a by-product of acetoacetic acid. Acetone is one of the ketone bodies produced in abnormal amounts in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, metabolic acidosis, pregnancy toxemia and ketosis of ruminants. Unlike the other ketone bodies, acetone cannot be used by the tissues to generate energy and is excreted as a waste product in the urine and by exhalation. The characteristic fruity odor on the breath of animals with ketosis is due to the exhalation of acetone. -tri-zo’āt] the sodium salt of acetrizoic acid, used as a contrast medium in radiography.
-tri-zo’āt] the sodium salt of acetrizoic acid, used as a contrast medium in radiography. -t
-t l, as″
l, as″ -tēl’ ko-a’] key intermediate in aerobic intermediary metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and some amino acids. Carrier of acetyl groups into the tricarboxylic acid (Krebs) cycle and the chief precursor of lipids; it is formed by the attachment to coenzyme A of an acetyl group during the oxidation of pyruvate, fatty acids or amino acids. The only intermediate used up (ie not re-generated) in the Krebs cycle. Allosteric regulator of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and pyruvate carboxylase. Present in low concentrations but with high turnover. Dependent on B-group vitamin, pantothenic acid for structure of coenzyme A.
-tēl’ ko-a’] key intermediate in aerobic intermediary metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and some amino acids. Carrier of acetyl groups into the tricarboxylic acid (Krebs) cycle and the chief precursor of lipids; it is formed by the attachment to coenzyme A of an acetyl group during the oxidation of pyruvate, fatty acids or amino acids. The only intermediate used up (ie not re-generated) in the Krebs cycle. Allosteric regulator of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and pyruvate carboxylase. Present in low concentrations but with high turnover. Dependent on B-group vitamin, pantothenic acid for structure of coenzyme A. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl’ko-a’ kahr-bok’s
-tēl’ko-a’ kahr-bok’s -lās] a biotincontaining enzyme which participates in the synthesis of fatty acids by catalyzing the carboxylation reaction in which acetyl-CoA is converted to malonyl-CoA. It has the important effect of regulating the rate of fatty acid synthesis and is itself influenced in its activity by the local concentration of magnesium, citrate, palmitylcarnitine and ATP and is stimulated by the action of insulin.
-lās] a biotincontaining enzyme which participates in the synthesis of fatty acids by catalyzing the carboxylation reaction in which acetyl-CoA is converted to malonyl-CoA. It has the important effect of regulating the rate of fatty acid synthesis and is itself influenced in its activity by the local concentration of magnesium, citrate, palmitylcarnitine and ATP and is stimulated by the action of insulin. -set″
-set″ -la’sh
-la’sh n] one of the synthetic biotransformations which operate in the metabolism of drugs in which metabolites are produced that are more readily excreted than the parent drug. Dogs are exceptional amongst the domesticated species in that acetylation does not occur in their tissues. Acetylation is one of the principal metabolic pathways of the sulfonamides.
n] one of the synthetic biotransformations which operate in the metabolism of drugs in which metabolites are produced that are more readily excreted than the parent drug. Dogs are exceptional amongst the domesticated species in that acetylation does not occur in their tissues. Acetylation is one of the principal metabolic pathways of the sulfonamides. -set″
-set″ -la’t
-la’t r] an organism capable of metabolic acetylation. Those animals that differ in their inherited ability to metabolize certain drugs, e.g. isoniazid, are termed fast or slow acetylators.
r] an organism capable of metabolic acetylation. Those animals that differ in their inherited ability to metabolize certain drugs, e.g. isoniazid, are termed fast or slow acetylators. -t
-t l kahr’n
l kahr’n -tēn] a substance which can act as a carrier for acetyl groups across the inner mitochondrial membrane in mammalian liver.
-tēn] a substance which can act as a carrier for acetyl groups across the inner mitochondrial membrane in mammalian liver. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl-ko’lēn] the acetic acid ester of choline, normally present in many parts of the body and having important physiological functions. It is a neurotransmitter at cholinergic synapses in the central, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. It is not used clinically but it is the classical cholinergic agonist.
-tēl-ko’lēn] the acetic acid ester of choline, normally present in many parts of the body and having important physiological functions. It is a neurotransmitter at cholinergic synapses in the central, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. It is not used clinically but it is the classical cholinergic agonist. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl-ko″l
-tēl-ko″l -nes’t
-nes’t -rās] an enzyme present in nervous tissue, muscle and red cells that catalyzes the hydrolysis of acetylcholine to choline and acetic acid; called also true cholinesterase.
-rās] an enzyme present in nervous tissue, muscle and red cells that catalyzes the hydrolysis of acetylcholine to choline and acetic acid; called also true cholinesterase. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl-sis’te-ēn] a mucolytic agent used to reduce the viscosity of secretions of the respiratory tract. The principal method of administration is by aerosol, which in animals requires the use of a face mask or aerosol chamber. Also used parenterally in the treatment of acetaminophen poisoning in cats where it aids in detoxification of the drug and enhances its elimination, and topically in the treatment of collagenase-associated corneal ulcers.
-tēl-sis’te-ēn] a mucolytic agent used to reduce the viscosity of secretions of the respiratory tract. The principal method of administration is by aerosol, which in animals requires the use of a face mask or aerosol chamber. Also used parenterally in the treatment of acetaminophen poisoning in cats where it aids in detoxification of the drug and enhances its elimination, and topically in the treatment of collagenase-associated corneal ulcers. -set’
-set’ -lēn] a colorless, combustible, explosive gas, the simplest triple-bonded hydrocarbon.
-lēn] a colorless, combustible, explosive gas, the simplest triple-bonded hydrocarbon. -t
-t l eth″
l eth″ l-en’
l-en’ -mēn] one of a group of related alkylating agents used in the preparation of inactivated vaccines.
-mēn] one of a group of related alkylating agents used in the preparation of inactivated vaccines. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl-gal″ak-tōs’
-tēl-gal″ak-tōs’ -mēn] one of the repeating disaccharide units in glycosaminoglycans.
-mēn] one of the repeating disaccharide units in glycosaminoglycans. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl″gloo-kōs’
-tēl″gloo-kōs’ -mēn sul’f
-mēn sul’f -tās] an enzyme which when deficient in Nubian goats causes a condition similar to Sanfilippo’s III-D syndrome in humans; the clinical syndrome includes delay in rising and walking in neonates, ataxia, bowing of front limbs, clouding of the cornea, dwarfism, and cartilaginous and bony deformities; histological examination reveals lysosomal overload.
-tās] an enzyme which when deficient in Nubian goats causes a condition similar to Sanfilippo’s III-D syndrome in humans; the clinical syndrome includes delay in rising and walking in neonates, ataxia, bowing of front limbs, clouding of the cornea, dwarfism, and cartilaginous and bony deformities; histological examination reveals lysosomal overload. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl-gloo’t
-tēl-gloo’t -māt] compound produced from acetyl CoA and glutamate that provides the regulator stimulus to the activity of carbamoyl synthetase II of the urea cycle.
-māt] compound produced from acetyl CoA and glutamate that provides the regulator stimulus to the activity of carbamoyl synthetase II of the urea cycle. -t
-t l-, as″
l-, as″ -tēl″stro-fan’th
-tēl″stro-fan’th -din] a semisynthetic cardiac glycoside, similar to strophanthin.
-din] a semisynthetic cardiac glycoside, similar to strophanthin. -la’zh
-la’zh ] failure to relax of the smooth muscle fibers of the gastrointestinal tract at any junction of one part with another; especially failure of the lower esophagus to relax with swallowing, due to an abnormality of innervation. Called also cardiospasm. See also megaesophagus.
] failure to relax of the smooth muscle fibers of the gastrointestinal tract at any junction of one part with another; especially failure of the lower esophagus to relax with swallowing, due to an abnormality of innervation. Called also cardiospasm. See also megaesophagus. -ki″ro-po’de-
-ki″ro-po’de- ] a developmental anomaly characterized by absence of all feet, both fore and hind.
] a developmental anomaly characterized by absence of all feet, both fore and hind.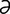 -kil’ēz] the group of tendons that insert on the calcaneus near the point of the hock made up of the tendons of the gastrocnemius, soleus, superficial digital flexor, semitendinosus and biceps femoris muscles. Called also common calcaneal tendon. See also gastrocnemius muscle tendon.
-kil’ēz] the group of tendons that insert on the calcaneus near the point of the hock made up of the tendons of the gastrocnemius, soleus, superficial digital flexor, semitendinosus and biceps femoris muscles. Called also common calcaneal tendon. See also gastrocnemius muscle tendon.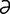 ] fungus which causes white, cotton-wool like growths on cutaneous trauma sites of fish and their newly spawned eggs; most common at colder water temperatures.
] fungus which causes white, cotton-wool like growths on cutaneous trauma sites of fish and their newly spawned eggs; most common at colder water temperatures. -sis] a hereditary disorder characterized by hypoplasia of bone, resulting in markedly shortened limbs; the head and trunk are normal.
-sis] a hereditary disorder characterized by hypoplasia of bone, resulting in markedly shortened limbs; the head and trunk are normal. ] a failure of growth of cartilage in the young, leading to a type of short-legged dwarfism. Several breeds of dogs display this in their standard conformation, e.g. Dachshund, Basset hound, Corgi. In dogs of this stature, this has been related to an extra copy of the gene that codes for a growth-promoting protein, called fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF-4). See also chondrodysplasia.
] a failure of growth of cartilage in the young, leading to a type of short-legged dwarfism. Several breeds of dogs display this in their standard conformation, e.g. Dachshund, Basset hound, Corgi. In dogs of this stature, this has been related to an extra copy of the gene that codes for a growth-promoting protein, called fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF-4). See also chondrodysplasia.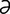 ] 1. lack of normal skin pigmentation. 2. the inability of tissues or cells to be stained.
] 1. lack of normal skin pigmentation. 2. the inability of tissues or cells to be stained.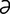 -kro’m
-kro’m -tiz-
-tiz- m] the quality or the condition of being achromatic; staining with difficulty.
m] the quality or the condition of being achromatic; staining with difficulty. -kro″m
-kro″m -to’sis] 1. deficiency of pigmentation in the tissues. 2. lack of staining power in a cell or tissue.
-to’sis] 1. deficiency of pigmentation in the tissues. 2. lack of staining power in a cell or tissue. ] loss or absence of pigment in hair. It may be complete or patchy, affect the length of the fiber or be in well-defined bands or speckled. Can be caused by nutritional deficiency, selective freezing, radiation or pressure. See also vitiligo, copper nutritional deficiency.
] loss or absence of pigment in hair. It may be complete or patchy, affect the length of the fiber or be in well-defined bands or speckled. Can be caused by nutritional deficiency, selective freezing, radiation or pressure. See also vitiligo, copper nutritional deficiency. ns] a state of equilibrium between acidity and alkalinity of the body fluids; called also hydrogen ion (H+) balance because, by definition, an acid is a substance capable of giving up a hydrogen ion during a chemical exchange, and a base is a substance that can accept it. The positively charged hydrogen ion (H+) is the active constituent of all acids. Most of the body’s metabolic processes produce acids as their end products, but a somewhat alkaline body fluid (pH 7.4) is required as a medium for vital cellular activities. Therefore chemical exchanges of hydrogen ions must take place continuously in order to maintain a state of equilibrium. An optimal pH (hydrogen ion concentration) between 7.35 and 7.45 must be maintained; otherwise, the enzyme systems and other biochemical and metabolic activities will not function normally. Although the body can tolerate and compensate for slight deviations in acidity and alkalinity, if the pH drops below 7.30, the potentially serious condition of acidosis exists. If the pH goes higher than 7.50, the patient is in a state of alkalosis. In either case the disturbance of the acid–base balance is considered serious, even though there are control mechanisms by which the body can compensate for an upward or downward change in the pH. Shifts in the pH of body fluids are controlled by three major regulatory systems which may be classified as chemical (the buffer systems), biological (blood and cellular activity), and physiological (the lungs and kidneys). The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is used to categorize four primary acidbase disturbances: respiratory acidosis (increased PCO2), respiratory alkalosis (decreased PCO2), metabolic acidosis (decreased extracellular base excess), or metabolic alkalosis (increased extracellular base excess). The anion gap is calculated to detect the presence of unidentified anions in plasma. This approach works well with clinical problems when serum total protein, albumin, and phosphate concentrations are approximately normal. The strong-ion difference method of evaluating acid-base balance, based on the concept that pH is primarily determined by PCO2, strong ion difference (SID), and nonvolatile buffer concentration (ATOT) and categorizes acid-base disturbances into six categories: respiratory acidosis and alkalosis, strong ion acidosis and alkalosis, nonvolatile buffer ion acidosis and alkalosis. It is recommended for use whenever serum total protein, albumin, and phosphate concentrations are markedly abnormal and where lactate, ketoacids, and uremic anions are contributory to the acid-base disturbance.
ns] a state of equilibrium between acidity and alkalinity of the body fluids; called also hydrogen ion (H+) balance because, by definition, an acid is a substance capable of giving up a hydrogen ion during a chemical exchange, and a base is a substance that can accept it. The positively charged hydrogen ion (H+) is the active constituent of all acids. Most of the body’s metabolic processes produce acids as their end products, but a somewhat alkaline body fluid (pH 7.4) is required as a medium for vital cellular activities. Therefore chemical exchanges of hydrogen ions must take place continuously in order to maintain a state of equilibrium. An optimal pH (hydrogen ion concentration) between 7.35 and 7.45 must be maintained; otherwise, the enzyme systems and other biochemical and metabolic activities will not function normally. Although the body can tolerate and compensate for slight deviations in acidity and alkalinity, if the pH drops below 7.30, the potentially serious condition of acidosis exists. If the pH goes higher than 7.50, the patient is in a state of alkalosis. In either case the disturbance of the acid–base balance is considered serious, even though there are control mechanisms by which the body can compensate for an upward or downward change in the pH. Shifts in the pH of body fluids are controlled by three major regulatory systems which may be classified as chemical (the buffer systems), biological (blood and cellular activity), and physiological (the lungs and kidneys). The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is used to categorize four primary acidbase disturbances: respiratory acidosis (increased PCO2), respiratory alkalosis (decreased PCO2), metabolic acidosis (decreased extracellular base excess), or metabolic alkalosis (increased extracellular base excess). The anion gap is calculated to detect the presence of unidentified anions in plasma. This approach works well with clinical problems when serum total protein, albumin, and phosphate concentrations are approximately normal. The strong-ion difference method of evaluating acid-base balance, based on the concept that pH is primarily determined by PCO2, strong ion difference (SID), and nonvolatile buffer concentration (ATOT) and categorizes acid-base disturbances into six categories: respiratory acidosis and alkalosis, strong ion acidosis and alkalosis, nonvolatile buffer ion acidosis and alkalosis. It is recommended for use whenever serum total protein, albumin, and phosphate concentrations are markedly abnormal and where lactate, ketoacids, and uremic anions are contributory to the acid-base disturbance. -tās] a lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyzes phosphate esters liberating phosphate, showing optimal activity at a pH between 3 and 6; found in erythrocytes, prostatic tissue, spleen, kidney and other tissues.
-tās] a lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyzes phosphate esters liberating phosphate, showing optimal activity at a pH between 3 and 6; found in erythrocytes, prostatic tissue, spleen, kidney and other tissues. -sid″
-sid″ -fi’
-fi’ r] an agent that causes acidity; a substance used to increase gastric or urine acidity.
r] an agent that causes acidity; a substance used to increase gastric or urine acidity. -sid’
-sid’ -te] 1. the quality of being acid; the power to unite with positively charged ions or with basic substances. 2. excess acid quality, as of the gastric juice.
-te] 1. the quality of being acid; the power to unite with positively charged ions or with basic substances. 2. excess acid quality, as of the gastric juice. -sid’o-fil″] 1. a histological structure, cell, or other element staining readily with acid dyes. 2. two types of cells in the pars distalis of the pituitary gland that secrete somatotropin and luteotropin. 3. an organism that grows well in highly acid media. 4. acidophilic.
-sid’o-fil″] 1. a histological structure, cell, or other element staining readily with acid dyes. 2. two types of cells in the pars distalis of the pituitary gland that secrete somatotropin and luteotropin. 3. an organism that grows well in highly acid media. 4. acidophilic. -do’sis] a pathological condition resulting from accumulation of acid or depletion of the alkaline reserve (bicarbonate content) in the blood and body tissues, and characterized by increase in hydrogen ion concentration (decrease in pH). The optimal acid–base balance is maintained by chemical buffers, biological activities of the cells, and effective functioning of the lungs and kidneys. The opposite of acidosis is alkalosis. It is rare that acidosis occurs in the absence of some underlying disease process. The more obvious signs of severe acidosis are muscle twitching, involuntary movement, cardiac arrhythmias, disorientation and coma.
-do’sis] a pathological condition resulting from accumulation of acid or depletion of the alkaline reserve (bicarbonate content) in the blood and body tissues, and characterized by increase in hydrogen ion concentration (decrease in pH). The optimal acid–base balance is maintained by chemical buffers, biological activities of the cells, and effective functioning of the lungs and kidneys. The opposite of acidosis is alkalosis. It is rare that acidosis occurs in the absence of some underlying disease process. The more obvious signs of severe acidosis are muscle twitching, involuntary movement, cardiac arrhythmias, disorientation and coma. -du’re-
-du’re- ] the excretion of acid in the urine. See also specific forms, such as aminoaciduria, orotic aciduria (below).
] the excretion of acid in the urine. See also specific forms, such as aminoaciduria, orotic aciduria (below). -net″o-bak’t
-net″o-bak’t r] gram-negative bacteria commonly found in the environment and often normal flora in animals and humans, but have been associated with nosocomial and opportunistic infections in a range of species with bronchopneumonia in mink and occasionally seen as a cause of bovine mastitis.
r] gram-negative bacteria commonly found in the environment and often normal flora in animals and humans, but have been associated with nosocomial and opportunistic infections in a range of species with bronchopneumonia in mink and occasionally seen as a cause of bovine mastitis. -n
-n s] pl. acini [L.] a small sac-like dilation; any of the smallest lobules of a compound gland.
s] pl. acini [L.] a small sac-like dilation; any of the smallest lobules of a compound gland. ] a genus of the plant family Apocynaceae used in Africa in the preparation of arrow poisons. Poisoned livestock show diarrhea, irregular heartbeat and sudden death. Contain cardiac glycosides. Includes A. longiflora, A. oblongifolia, A. oppositifolia, A. schimperi, A. spectabilis (A. oblongifolia), A. venenata (A. oppositifolia). Some species were formerly classified in Carissa spp.
] a genus of the plant family Apocynaceae used in Africa in the preparation of arrow poisons. Poisoned livestock show diarrhea, irregular heartbeat and sudden death. Contain cardiac glycosides. Includes A. longiflora, A. oblongifolia, A. oppositifolia, A. schimperi, A. spectabilis (A. oblongifolia), A. venenata (A. oppositifolia). Some species were formerly classified in Carissa spp. -kon’
-kon’ -tin] a mixture of alkaloids in Aconitum napellus. Causes abdominal pain, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, cardiac irregularity.
-tin] a mixture of alkaloids in Aconitum napellus. Causes abdominal pain, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, cardiac irregularity. -ni’t
-ni’t m] a genus of the Ranunculaceae family from northern temperate areas. Includes A. brachypodium, A. carmichaelii, A. chasmanthum, A. columbianum, A. ferox, A. lycoctonum, A. vaccarum, A. vulpari.
m] a genus of the Ranunculaceae family from northern temperate areas. Includes A. brachypodium, A. carmichaelii, A. chasmanthum, A. columbianum, A. ferox, A. lycoctonum, A. vaccarum, A. vulpari.